MATLAB学习笔记(二) 编写脚本与m文件
1.脚本script
1.1第一个脚本
for i=1:10
x=linspace(0,10,101);
plot(x,sin(x+i));
print(gcf,'-deps',strcat('plot',num2str(i),'.ps'));
endRun,快捷键为F5。
善用上方的插入、查找功能!
Ctrl+R,注释;Ctrl+T,取消注释。 %百分号为注释符!
%%,两对百分比符号之间的为“节”,可以单独运行节,利于debug!但“运行”按钮还是执行整个脚本。
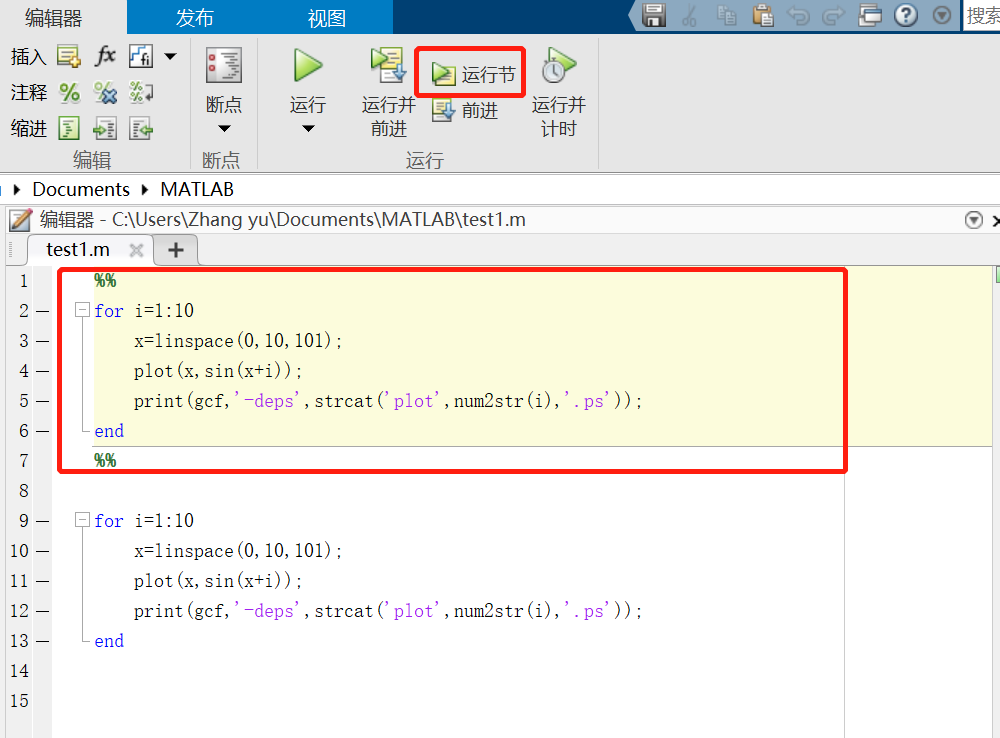
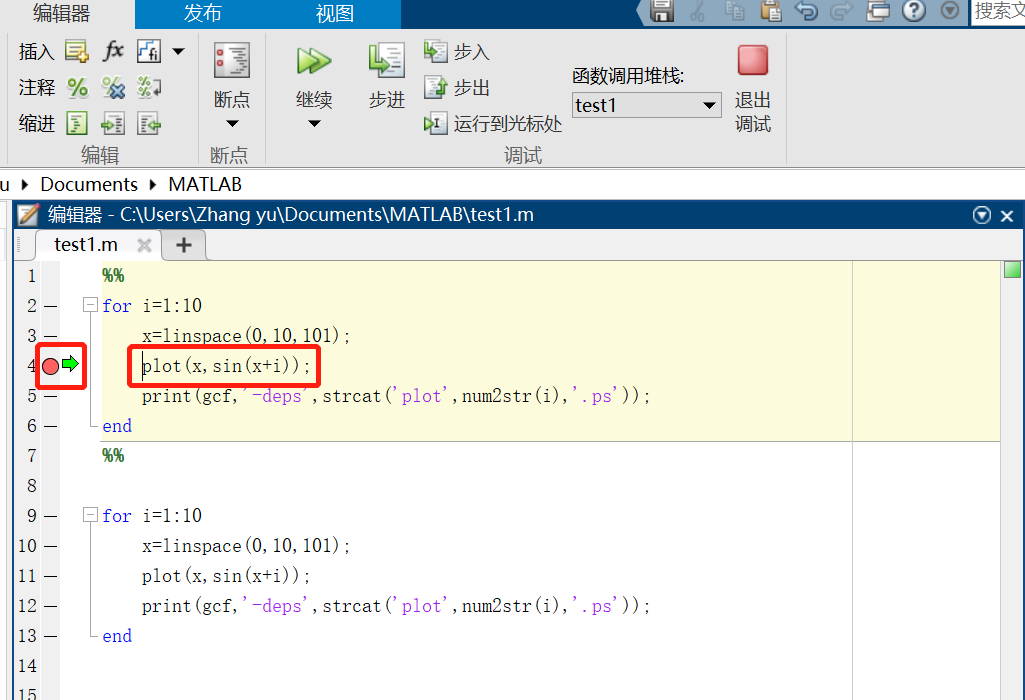
进入debug模式时,运行按钮会变成继续,鼠标放置到中断点时会显示内容!
Ctrl+I,智能缩进!
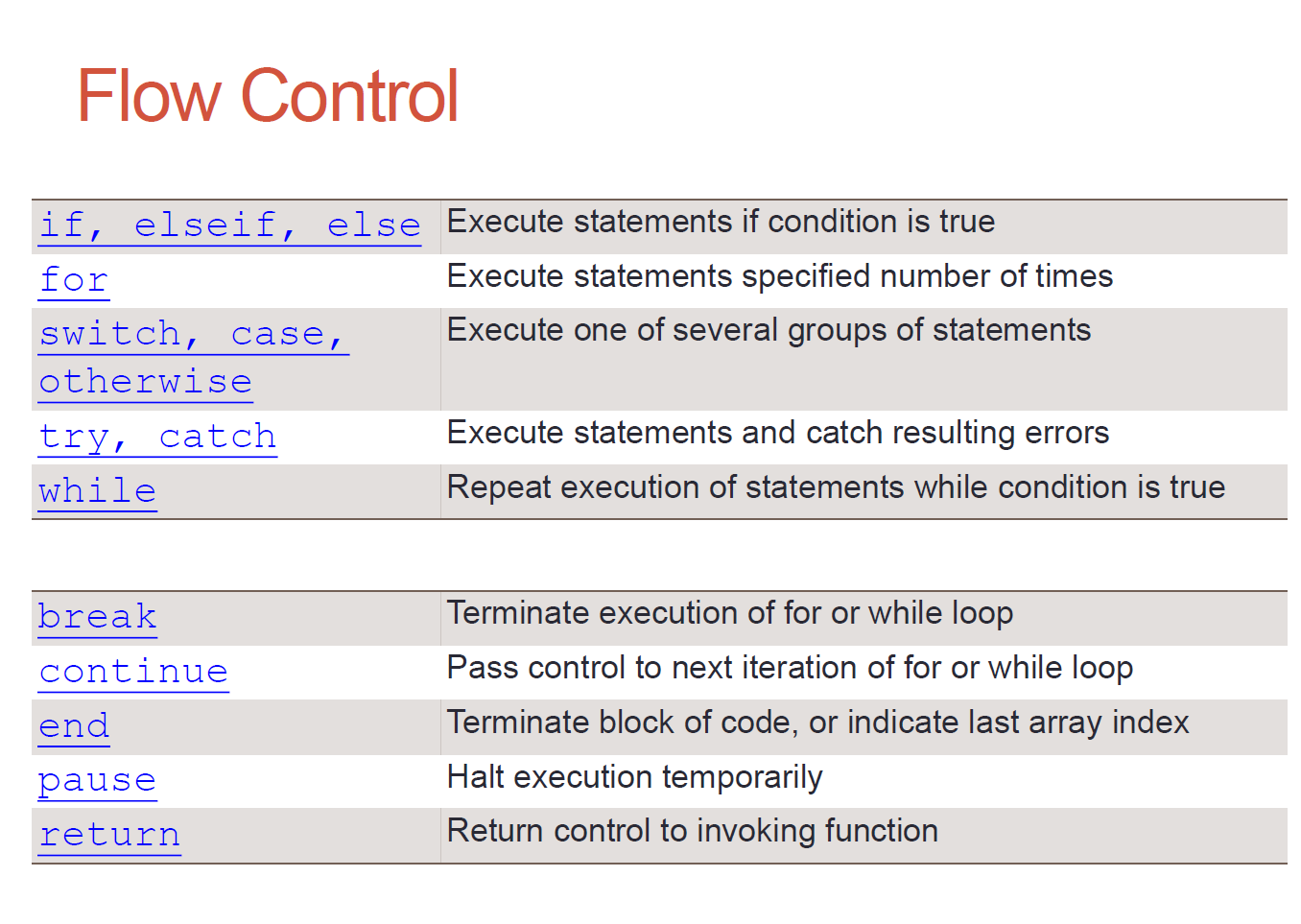
1.2Structured programming
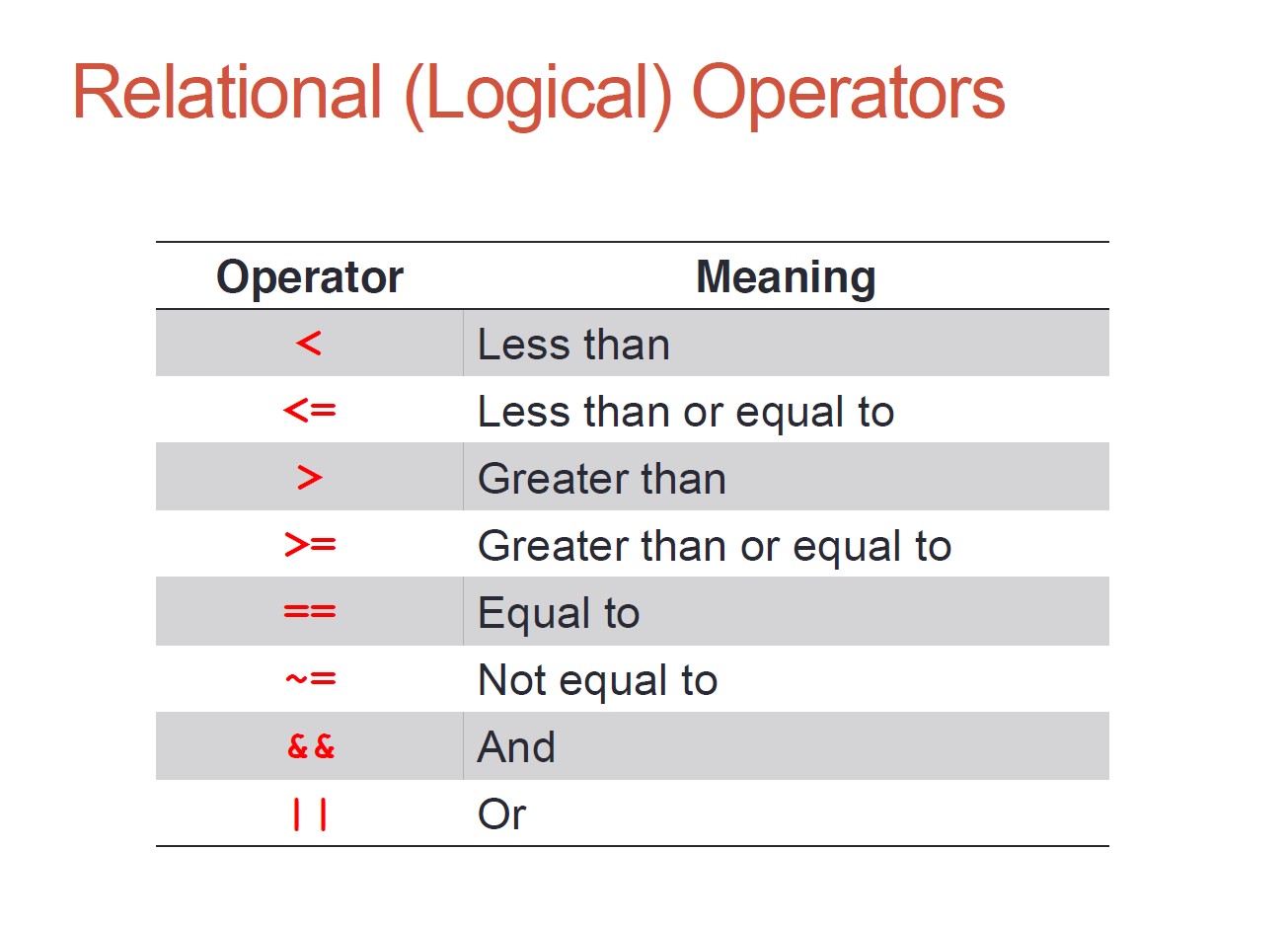
逻辑运算符 Relation(logical) operator
1.2.1 if elseif else
a = 3;
if rem(a, 2) == 0
disp('a is even')
else
disp('a is odd')
endrem(a, 2) 表示求a除以2的余数 rem=remainder; odd为奇数
1.2.2 switch
switch input_num %比如5
case -1
disp('negative 1');
case 0
disp('zero');
case 1
disp('positive 1');
otherwise
disp('other value');
end1.2.3 wihle
while expression
statement
end
n = 1;
while prod(1:n) < 1e100
n = n + 1;
end
n %表示输出最后的n,不然不输出内容prod 为求乘函数,示例为n的阶乘。
1e100 表示1*10的100次方,此例n+1=70
练习:计算1+2+3+…+999
s=0;
n=1;
while n<1000
s=s+n;
n=n+1;
end
disp(s)也可以这么写:
a = [1:999]
sum(a)1.2.4 for
for n = 1:10
a(n) = 2^n
end
disp(a)输出奇数次方:
for n=1:2:10
a((n+1)/2) = 2^n
end
disp(a)1.2.5 break
x = 2; k = 0; error = inf;
error_threshold = 1e-32;
while error > error_threshold
if k > 100
break
end
x = x - sin(x)/cos(x);
error = abs(x - pi);
k = k + 1;
end1.3 预先分配内存与运算时间
%%
tic
for ii = 1:2000
for jj = 1:2000
A(ii,jj) = ii + jj;
end
end
toc
%%
历时 2.989049 秒。
%%
tic
A = zeros(2000, 2000);
for ii = 1:size(A,1)
for jj = 1:size(A,2)
A(ii,jj) = ii + jj;
end
end
toc
%%
历时 0.026128 秒。close all 关闭所有图形
Ctrl+C,停止命令
… 换行号
A = [1 2 3; ...
4 5 6]
与↓相同(新版本可以直接换行)
A = [1 2 3; 4 5 6]2.函数
edit(which('mean.m'))调出mean的用法:
function y = mean(x,dim,flag,flag2)
%MEAN Average or mean value.
% S = MEAN(X) is the mean value of the elements in X if X is a vector.
% For matrices, S is a row vector containing the mean value of each
% column.
% For N-D arrays, S is the mean value of the elements along the first
% array dimension whose size does not equal 1.
%
% MEAN(X,'all') is the mean of all elements in X.
%
% MEAN(X,DIM) takes the mean along the dimension DIM of X.
%
% MEAN(X,VECDIM) operates on the dimensions specified in the vector
% VECDIM. For example, MEAN(X,[1 2]) operates on the elements contained
% in the first and second dimensions of X.
%
% S = MEAN(...,TYPE) specifies the type in which the mean is performed,
% and the type of S. Available options are:
%
% 'double' - S has class double for any input X
% 'native' - S has the same class as X
% 'default' - If X is floating point, that is double or single,
% S has the same class as X. If X is not floating point,
% S has class double.
%
% S = MEAN(...,NANFLAG) specifies how NaN (Not-A-Number) values are
% treated. The default is 'includenan':
%
% 'includenan' - the mean of a vector containing NaN values is also NaN.
% 'omitnan' - the mean of a vector containing NaN values is the mean
% of all its non-NaN elements. If all elements are NaN,
% the result is NaN.
%
% Example:
% X = [1 2 3; 3 3 6; 4 6 8; 4 7 7]
% mean(X,1)
% mean(X,2)
%
% Class support for input X:
% float: double, single
% integer: uint8, int8, uint16, int16, uint32,
% int32, uint64, int64
%
% See also MEDIAN, STD, MIN, MAX, VAR, COV, MODE.
% Copyright 1984-2018 The MathWorks, Inc.
isDimSet = nargin > 1 && ((~ischar(dim) && ~(isstring(dim) && isscalar(dim))) || ...
(~isInvalidText(dim) && strncmpi(dim,'all',max(strlength(dim), 1))));
isFlag2Set = nargin >= 4;
if nargin == 1 || (nargin == 2 && isDimSet)
flag = 'default';
omitnan = false;
else % nargin >= 3 || (nargin == 2 && ~isDimSet)
if nargin == 2
flag = dim;
elseif nargin == 3
if ~isDimSet
flag2 = dim;
isFlag2Set = true;
end
elseif nargin == 4 && ~isDimSet
error(message('MATLAB:mean:nonNumericSecondInput'));
end
if ~isFlag2Set
flag2 = '';
end
[flag, omitnan] = parseInputs(flag, flag2, isFlag2Set);
end
if ~isDimSet
% preserve backward compatibility with 0x0 empty
if isequal(x,[])
y = sum(x,flag)./0;
return
end
dim = find(size(x)~=1,1);
if isempty(dim)
dim = 1;
end
else
if isempty(dim)
error(message('MATLAB:mean:nonNumericSecondInput'));
end
end
if ~isobject(x) && isinteger(x)
% accumulation flag may still be partial
isnative = strncmpi(flag, 'native', max(1, strlength(flag)));
if intmin(class(x)) == 0 % unsigned integers
y = sum(x,dim,flag);
if (isnative && all(y(:) < intmax(class(x)))) || ...
(~isnative && all(y(:) <= flintmax))
% no precision lost, can use the sum result
y = y./mysize(x,dim);
else % throw away and recompute
y = intmean(x,dim,isnative);
end
else % signed integers
ypos = sum(max(x,0),dim,flag);
yneg = sum(min(x,0),dim,flag);
if (isnative && all(ypos(:) < intmax(class(x))) && ...
all(yneg(:) > intmin(class(x)))) || ...
(~isnative && all(ypos(:) <= flintmax) && ...
all(yneg(:) >= -flintmax))
% no precision lost, can use the sum result
y = (ypos+yneg)./mysize(x,dim);
else % throw away and recompute
y = intmean(x,dim,isnative);
end
end
else
if omitnan
% Compute sum and number of NaNs
m = sum(x, dim, flag, 'omitnan');
nr_nonnan = mysize(x, dim) - matlab.internal.math.countnan(x, dim);
% Divide by the number of non-NaNs.
y = m ./ nr_nonnan;
else
y = sum(x, dim, flag) ./ mysize(x,dim);
end
end
end
function y = intmean(x, dim, isnative)
% compute the mean of integer vector
ysiz = size(x);
if ischar(dim) || isstring(dim)
x = x(:);
else
dim = reshape(dim, 1, []);
dim = min(dim, ndims(x)+1);
if max(dim)>length(ysiz)
ysiz(end+1:max(dim)) = 1;
end
tf = false(size(ysiz));
tf(dim) = true;
r = find(~tf);
perm = [find(tf), r];
x = permute(x, perm);
x = reshape(x,[prod(ysiz(dim)), prod(ysiz(r))]);
ysiz(dim) = 1;
end
xclass = class(x);
if ~isnative
outclass = 'double';
else
outclass = xclass;
end
if intmin(xclass) == 0
accumclass = 'uint64';
else
accumclass = 'int64';
end
xsiz = size(x);
xlen = cast(xsiz(1),accumclass);
y = zeros([1 xsiz(2:end)],outclass);
ncolumns = prod(xsiz(2:end));
int64input = isa(x,'uint64') || isa(x,'int64');
for iter = 1:ncolumns
xcol = cast(x(:,iter),accumclass);
if int64input
xr = rem(xcol,xlen);
ya = sum((xcol-xr)./xlen,1,'native');
xcol = xr;
else
ya = zeros(accumclass);
end
xcs = cumsum(xcol);
ind = find(xcs == intmax(accumclass) | (xcs == intmin(accumclass) & (xcs < 0)) , 1);
while (~isempty(ind))
remain = rem(xcs(ind-1),xlen);
ya = ya + (xcs(ind-1) - remain)./xlen;
xcol = [remain; xcol(ind:end)];
xcs = cumsum(xcol);
ind = find(xcs == intmax(accumclass) | (xcs == intmin(accumclass) & (xcs < 0)), 1);
end
if ~isnative
remain = rem(xcs(end),xlen);
ya = ya + (xcs(end) - remain)./xlen;
% The latter two conversions to double never lose precision as
% values are less than FLINTMAX. The first conversion may lose
% precision.
y(iter) = double(ya) + double(remain)./double(xlen);
else
y(iter) = cast(ya + xcs(end) ./ xlen, outclass);
end
end
if ~isscalar(y)
y = reshape(y,ysiz);
end
end
function [flag, omitnan] = parseInputs(flag, flag2, isFlag2Set)
% Process flags, return boolean omitnan and string flag
if isInvalidText(flag)
error(message('MATLAB:mean:invalidFlags'));
end
if isstring(flag)
flag = char(flag);
end
s = strncmpi(flag, {'omitnan', 'includenan'}, max(length(flag), 1));
if ~isFlag2Set
omitnan = s(1);
if any(s)
flag = 'default';
end
else
if isInvalidText(flag2)
error(message('MATLAB:mean:invalidFlags'));
end
if isstring(flag2)
flag2 = char(flag2);
end
s2 = strncmpi(flag2, {'omitnan', 'includenan'}, max(length(flag2), 1));
% Make sure one flag is from the set {'omitnan', 'includenan'},
% while the other is from {'default', 'double', 'native'}.
if ~xor( any(s), any(s2) )
error(message('MATLAB:mean:invalidFlags'));
end
if any(s) % flag contains 'includenan' or 'omitnan'
omitnan = s(1);
flag = flag2;
else
omitnan = s2(1);
end
end
end
function tf = isInvalidText(str)
tf = (ischar(str) && ~isrow(str)) || ...
(isstring(str) && ~(isscalar(str) && (strlength(str) > 0)));
end
function s = mysize(x, dim)
if isnumeric(dim) || islogical(dim)
if isscalar(dim)
s = size(x,dim);
else
s = size(x,dim(1));
for i = 2:length(dim)
s = s * size(x,dim(i));
end
end
else
s = numel(x);
end
end2.1自定义函数
如,新建自由落体运动的计算公式:
function x = freebody(x0,v0,t)
% calculation of free falling
% x0: initial displacement in m
% v0: initial velocity in m/sec
% t: the elapsed time in sec
% x: the depth of falling in m
x = x0 + v0.*t + 1/2*9.8*t.*t; %此处选择点乘,可以多组数据一起运算(向量同样适用)需要将文件保存成与函数名相同的名称!
此时左下角会出现函数名!
2.2Functions with Multiple Inputs and Outputs
function [a F] = acc(v2,v1,t2,t1,m)
a = (v2-v1)./(t2-t1);
F = m.*a;[Acc Force] = acc(20,10,5,4,1)2.3Function Default Variables
function [volume]=pillar(Do,Di,height)
if nargin==2,
height=1;
end
volume=abs(Do.^2-Di.^2).*height*pi/4;2.4Function Handles
函数指针?
f = @(x) exp(-2*x);
x = 0:0.1:2;
plot(x, f(x));本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-SA 4.0 协议 ,转载请注明出处!